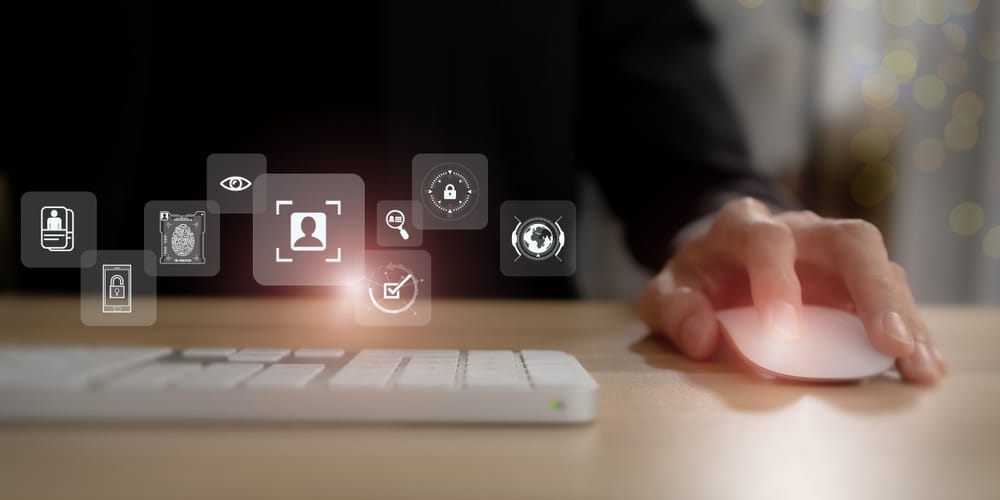
Ensuring Data Privacy in KYC Compliance: Key Steps and Best Practices
Data privacy compliance is a critical aspect of operating in today’s digital landscape. Protecting personal data and adhering to regulatory requirements helps build trust with customers and avoid legal repercussions. Implementing key steps and best practices for data privacy compliance ensures that organizations handle personal data responsibly.
Key Steps for Data Privacy Compliance
1. Understand Applicable Regulations
Description: Familiarize yourself with data privacy regulations applicable to your organization.
Steps:
- Identify Regulations: Determine which regulations apply based on your location and the nature of your business (e.g., GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA).
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of updates and changes to these regulations.
- Seek Legal Advice: Consult with legal experts to understand your obligations.
Benefits:
- Compliance: Ensures that your organization meets legal requirements.
- Risk Reduction: Reduces the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
2. Conduct Data Privacy Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
Description: DPIAs help identify and mitigate data protection risks in new projects or processes.
Steps:
- Identify Risks: Assess the potential impact on data privacy and security.
- Mitigate Risks: Implement measures to mitigate identified risks.
- Document Findings: Maintain records of the assessment and mitigation measures.
Benefits:
- Proactive Risk Management: Helps identify and address risks before they become issues.
- Compliance: Ensures compliance with regulatory requirements for risk assessment.
3. Implement Data Minimization
Description: Collect only the data necessary for the specific purpose.
Steps:
- Define Purpose: Clearly define the purpose of data collection.
- Limit Collection: Collect only the data needed for that purpose.
- Regular Review: Periodically review data collection practices to ensure they align with the principle of data minimization.
Benefits:
- Security: Reduces the risk of data breaches by minimizing the amount of data collected.
- Compliance: Aligns with data privacy principles and regulations.
4. Secure Data Storage and Transmission
Description: Implement robust security measures to protect personal data during storage and transmission.
Steps:
- Encryption: Use encryption to protect data at rest and in transit.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit who can access personal data.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Benefits:
- Protection: Protects personal data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Trust: Builds trust with customers by ensuring their data is secure.
Best Practices for Data Privacy Compliance
1. Establish a Data Privacy Policy
Description: Develop a comprehensive data privacy policy that outlines how personal data is collected, used, and protected.
Steps:
- Policy Development: Create a clear and concise data privacy policy.
- Employee Training: Train employees on the policy and their responsibilities.
- Public Disclosure: Make the policy available to customers and stakeholders.
Benefits:
- Transparency: Demonstrates your commitment to data privacy.
- Accountability: Holds your organization accountable for protecting personal data.
2. Implement Consent Management
Description: Obtain and manage consent for data collection and processing.
Steps:
- Clear Consent Requests: Use clear and understandable language when requesting consent.
- Granular Consent: Allow users to provide consent for specific data processing activities.
- Manage Preferences: Provide users with the ability to manage and withdraw their consent.
Benefits:
- Compliance: Ensures compliance with data privacy regulations requiring consent.
- User Control: Empowers users to control their personal data.
3. Regularly Review and Update Practices
Description: Continuously review and update your data privacy practices to stay compliant with evolving regulations.
Steps:
- Periodic Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of your data privacy practices.
- Stay Informed: Stay updated on changes to data privacy regulations.
- Implement Changes: Update your practices as needed to remain compliant.
Benefits:
- Adaptability: Ensures your organization can adapt to regulatory changes.
- Continuous Improvement: Promotes ongoing improvement of data privacy practices.
4. Provide Data Privacy Training
Description: Educate employees about data privacy and their responsibilities.
Steps:
- Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs for all employees.
- Regular Updates: Update training materials regularly to reflect regulatory changes and emerging trends.
- Interactive Sessions: Use interactive sessions, case studies, and simulations to enhance learning.
Benefits:
- Knowledgeable Staff: Ensures employees understand data privacy requirements and best practices.
- Improved Compliance: Enhances the ability to detect and report privacy issues.
- Compliance Culture: Fosters a culture of data privacy within the organization.
Ensuring data privacy compliance requires a proactive approach involving understanding regulations, conducting DPIAs, implementing data minimization, securing data storage and transmission, and establishing a comprehensive data privacy policy. By following these key steps and best practices, organizations can protect personal data, meet regulatory requirements, and build trust with customers.