Trusted by AML Compliance Leaders Worldwide

Start your free trial of iComply
Cancel Anytime. No Questions Asked.
Compliance Failures Cost Time, Money, & Trust
Disjointed Vendors
Complicates operations, drains development resources, and introduces risk
Manual Processes
Limits growth, requires excessive workforce resources, and increases human error
Negative Customer Experiences
Erodes trust, brand value, and competitive advantage
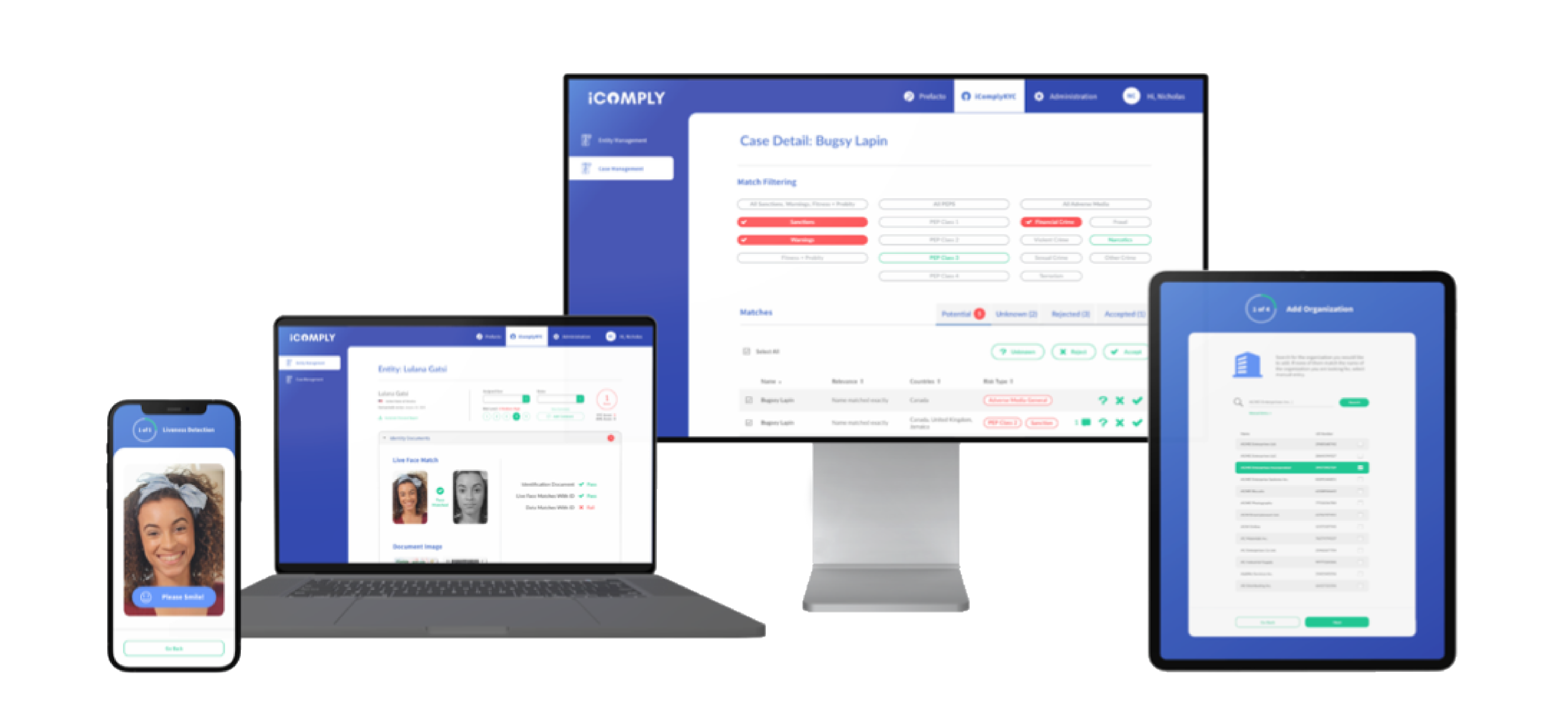
Streamlined AML Software for KYB, KYC, & KYT
Eliminate Vendor Complexity
Create your ideal solution – Deploy our turn-key AML software in days or request customizations unique to your requirements
Boost Efficiency & Effectiveness by up to 90%
Configure intuitive workflows and automation to apply your policies and procedures at scale
Improve Customer Satisfaction by over 25%
Offer a white-glove customer experience using our white-labelled onboarding portals

World-Class Privacy, Security, & Encryption
Adhere to data protection regulations including SOC2 and ISO 27001, CCPA, GDPR, PPIA, PIPEDA, PCI, and more.
Process and secure all sensitive data, documents, and biometrics on the user’s own device, not our servers, using the power of edge computing.
Leverage best practices with end-to-end encryption (TLS1.2, SSL, AES256) to store member data on your servers or clouds.
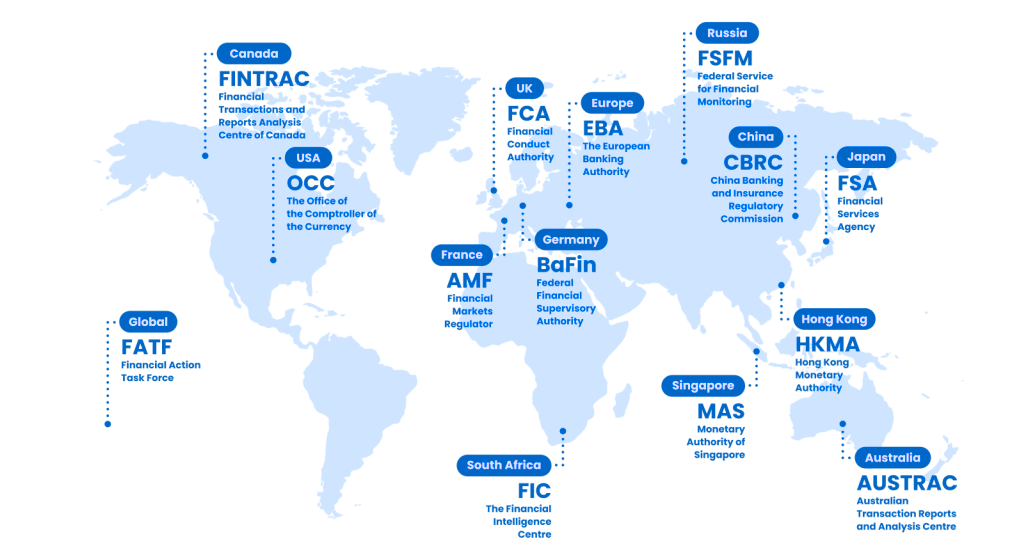
Global AML Compliance
Streamline and automate compliance in 195 countries.
14,000+ Identity Verification Documents
3,000+ Watchlists for Sanctions Screening
11,000+ Trusted Sources for Adverse Media Checks
PEPs Class 1-4: Politically Exposed Persons
We have settled in with your service and are very impressed. I have every confidence in iComply for the UK, where increasing pressure from regulators to not only improve AML compliance, but also to be able to demonstrate it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Learn more about about AML compliance, customer due diliegnce, and how iComply can support your business
Start your free trial of iComply
Cancel Anytime. No Questions Asked.