Trusted by Leaders in AML Compliance Over 30 Countries



Get started with iComply today
Replace fragmented tools and reduce your total cost of compliance up to 90%..
What Our Customers Are Saying
“We have settled in with your service and are very impressed. I have every confidence in iComply for the UK, where increasing pressure from regulators to not only improve AML compliance, but also to be able to demonstrate it.”

Go Live In 195 Countries
Choose the right deployment option that fits your unique requirements.
-
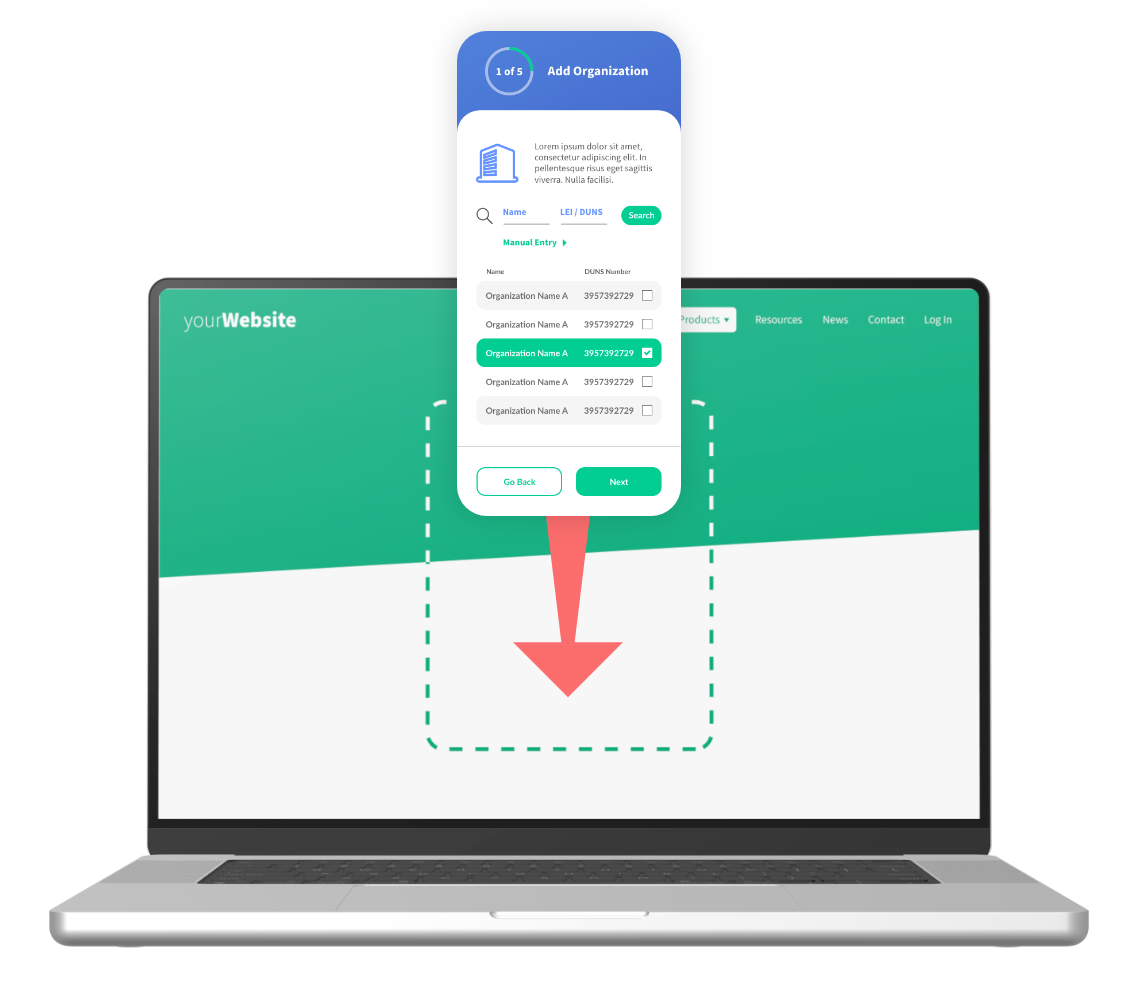
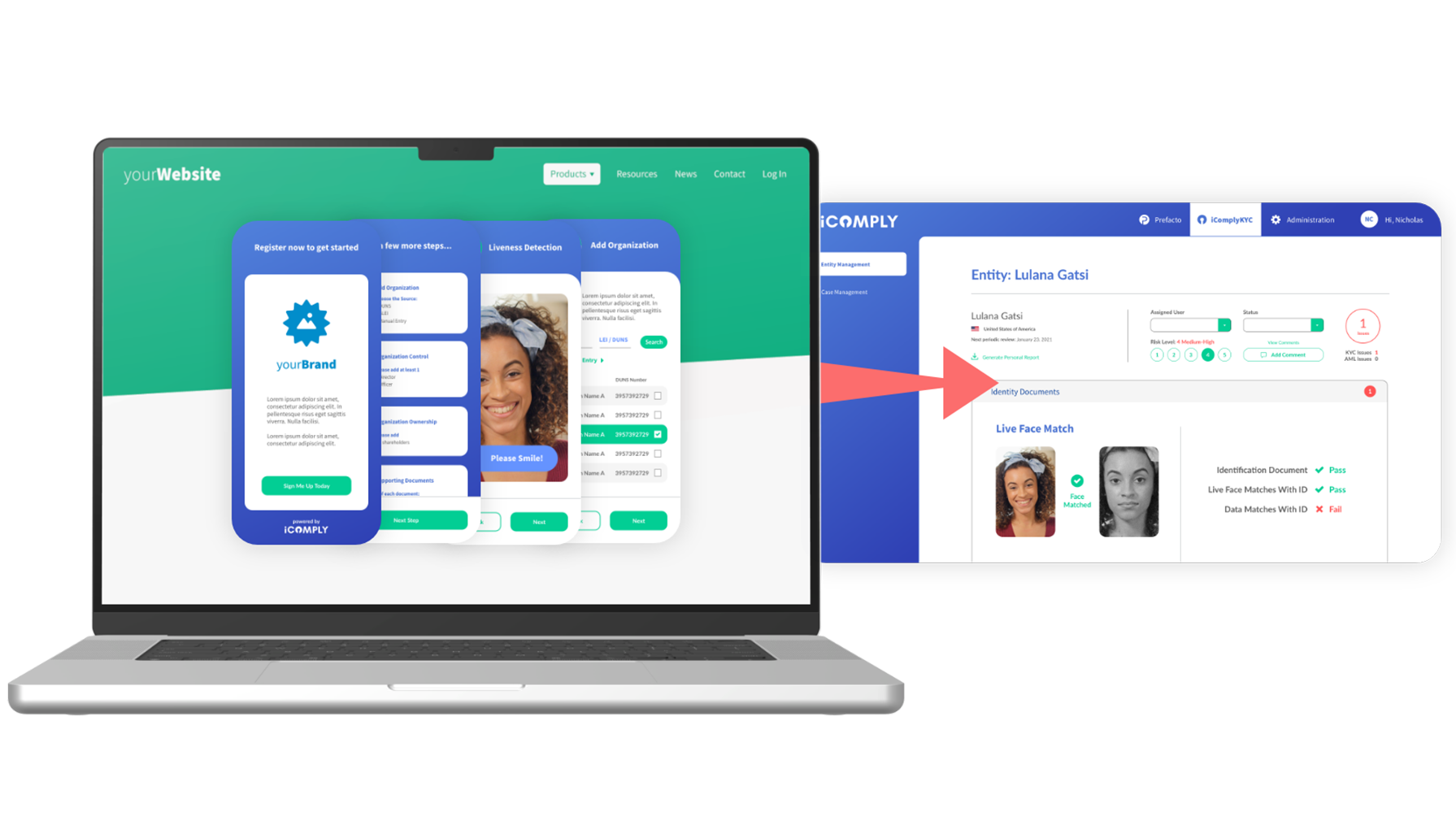
Instant SaaS onboarding — Get started in minutes with our no-code console and white-label KYC and KYB solutions.
-
Embedded applications — Integrate with your workflows into any web or mobile app using our plug-and-play SDKs.
-
Custom integrations — Use our secure and encrypted APIs to tailor onboarding, monitoring, and verification flows.
-
Enterprise deployments — Launch iComply in a private cloud or on-premise environment with custom controls.

The Status Quo in AML Compliance Solutions is Broken
Here’s how iComply is changing the game
Top 5 Pain Points in AML Compliance
Disconnected tools and vendors
Manual onboarding, refresh, and reviews
High false positive rates
Limited jurisdictional coverage
Offshore data processing and storage
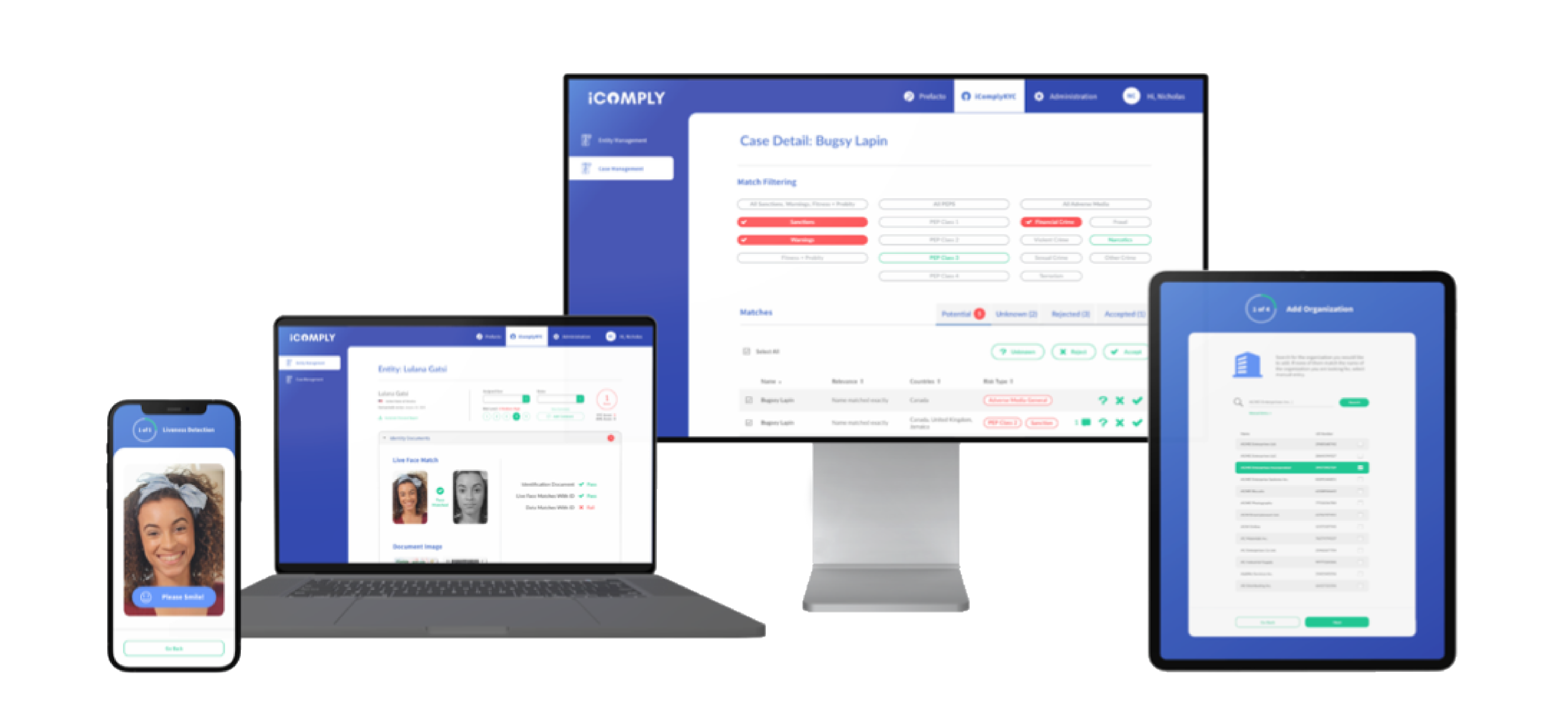
How iComply Creates Value
One modular platform
Automated onboarding, refresh, and reviews
Better signals, less noise
True global coverage
Edge-computing for local processing and storage
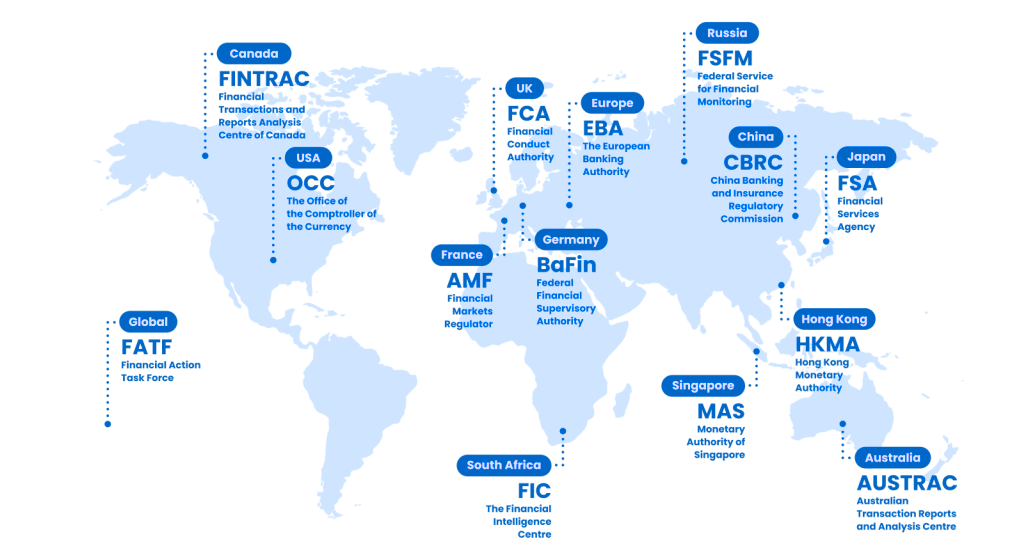
Your Customers Are Global, Your AML Software Should Be Too
Streamline and automate compliance operations for KYT, KYC, KYB, AML, data privacy and security.
Local data processing and encryption in 195 countries
14,000+ Identity Documents Templates
3,000+ Sanctions and Watchlists for Risk Screening
11,000+ Trusted Sources for Adverse Media Checks
300+ Million Corporate & Legal Entity Profiles
142 Officially Recognized National Languages
SaaS, Private Cloud, or On-Premise Deployment

Automate 90% of compliance operations with 90 days
Stop the busywork. Scale faster with an end-to-end, global compliance platform.
Global Updates and Insights for Leaders in AML Compliance

Solutions Tailored to Your Industry
iComply’s flexible KYT, KYC, KYB, AML compliance software easily adapts to the unique industry requirements of:
-
Money Services Businesses (MSBs & MTLs)
-
Legal & Accounting Firms
-
Commercial Banking & Insurance FIs
-
Financial Services Providers (FSPs)
- Fintech, Wealthtech, & Proptech
- Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs)

Still Have Questions?
Find answers to frequently asked questions about setup, features, and compliance capabilities.
Simple, Transparent Pricing
Whether you’re a startup or an enterprise, we have an end-to-end AML compliance solution to fit your needs for as little as $1 per entity per year:
-
-
Essentials – Core functionality for early-stage teams with onboarding, verification, and refresh workflows.
-
Plus – Enhanced automation, more volume, and global flexibility for 195 countries.
-
Pro – Advanced features including KYT transaction monitoring, and volume based pricing tiers.
-
Enterprise – Tailored deployments to your preferred data centre, dedicated success managers, and enterprise SLAs.
-